Sunday, March 22, 2009
Quiz for Case Study
What were the major drivers of the outsourcing at Kone?
Answer:
Major drives of the outsourcing at Kone are the realization of the unimportantness of internal IT processes to support the expansion of company, insufficient value-added private communication networks and unability to reduce the administrative cost by global sales by using IT.
Question 2:
Why did Kone elect to work with several vendors?
Answer:
Kone elect to work with several vendors because Kone believe using different vendors promised best-of-breed approach.
Question 3:
What are some of the risks of this outsourcing?
Answer:
Some of the risks of this outsourcing that Kone might have are the capability of both vendors to work together without any conflict, the ability of hardware provided by HP to adapt with SAP software and determination on those who responsible to take action if both hardware and software crashed.
Question 4:
How can Kone control its vendors?
Answer:
Kone control its vendors by making division of jobs clearly, always meet both team online and ensure that both HP and SAP work closely together.
Saturday, February 7, 2009
intro n history (Aziz)
What is transportation?
Transport or transportation is the movement of people and goods from one place to another. The term is derived from the Latin trans ("across") and portare ("to carry"). Transports have many categories such as Animal-powered transport, Aviation, Cable transport, Human-powered transport, Hybrid transport and Ship transport. Industries which have the business of providing equipment, actual transport, or goods and services used in transport of goods or people make up a large broad and important sector of most national economies, and are collectively referred to as transport industries.
What is courier?
The basic definition of "courier" is simply someone who delivers something from one place to another place. A courier is a messenger, conveying something of importance from the sending source to the receiving source. Within this definitive context, couriers and courier services can come in many different types and styles. In past times, before there were vehicles, couriers were usually just individual messengers, who traveled from one place to another to deliver news, documents, or products. Examples of this were the courier services of medieval times, which were one or more people who delivered messages or goods on horseback, or the famous pony express riders, who relayed messages or goods across the United States by passing them along from rider to rider until they reached their destination. Stage coaches were also used by courier services, as well as trains after they started coming into regular use. As time progressed and the age of technology set in, courier services began to use vehicles such as automobiles, modern trains, and airplanes. Suddenly the words "overnight" and "express" were starting to be used on a regular basis by courier services. Where once it would have taken days, weeks, or months for documents or products to be delivered, suddenly it was all becoming much more streamlined. Running a company that provided courier services was also becoming a lucrative prospect.
Types of courier services
There are as many different types of courier services as there are ways to carry messages, documents, and products. Of course, one permanently established courier service is the postal service. There are very few places in the world where mail cannot be delivered by the postal services of the various countries, especially with ever improving modern technology. The postal service is always a government run courier agency, however.
There are also many other large established privately run courier services, most of which now offer not only ground courier service, but express and overnight service. These large companies ship packages and documents all over the world - usually they can deliver any shipment that the post office can deliver.
Courier services do not have to be on a global scale, nor do they have to be only for packages and documents. In many large cities, there are courier services that actually use individual people that carry documents and messages across town. "Bike messengers" in New York City are a good example of this. When one company needs papers signed by someone in one of their across-town offices or by someone in another company, and the papers can't be faxed for some reason, or it is not papers but a package, a bike messenger can be sent. These messengers will race across town to deliver the goods from one place to another.
Standard courier services
The standard courier services that most of us are familiar with are the ones that can involve shipping to places all over the world. These companies have processes and steps that they take to make sure that documents and packages get safely and securely from one place to another. Though from the consumer's point of view the process of sending documents or packages is pretty straightforward - you give something to the courier service and it arrives where you send it - the actual process is much more involved. For instance, when you bring a package to a large courier service, the first thing that they will do is take down the pertinent information your name and address will also be placed on the package. The courier service will document information on the package weight, and charges will be applied accordingly. Most packages are automatically insured up to a certain amount, but you can insure it for more if what you are sending is more valuable than that. If you do need more insurance, then an extra charge will probably be added to the shipping price. The price will also be adjusted according to how fast you would like the package to arrive at its destination. Overnight and express shipping will, of course, cost more. Once all of this is determined, the package is then sent by truck, and if necessary, by plane also.
Overnight and same day courier services
There are courier services that specialize in overnight and express shipping. Though you will pay more for this type of courier service, it is often worth it when you want to make sure that something is going to arrive in a very short amount of time. Though almost all large worldwide courier services will provide overnight and express shipping, there are companies that have specialized in this type of service all along. Making sure that a package or document arrives overnight is no small feat. When you are sending a package from Los Angeles, California to St. Louis, Missouri and you want it to get there overnight, several factors have to come into place. For one thing, you want to make sure to get the package to the courier service as early as possible to ensure overnight or even express delivery. Though it is possible to get something shipped overnight even if you ship it late, the cost could go up considerably.
Packages that are shipped express or overnight are almost always flown to their destinations. One exception would be if you were only shipping to a place that was such a small distance away that shipment by plane would not be necessary. Although packages can be shipped using normal passenger airlines, most large courier services have their own fleet of planes, often called "cargo planes", that are for shipment purposes only.
Personal courier services
Personal courier services are usually defined as those services that send actual "messengers" from one place to another. As in the bike messenger example, the courier is usually only one person, and this person takes the message, package, or document from one place and delivers it personally to another place. These, of course, are smaller courier companies, and in some instances may involve only a few people who provide this service to established clients on a regular basis. When a company has a main headquarters in one part of a city, and an office on the other side of town, or a couple towns away, they can give a package or documents to a personal courier and this courier will use a vehicle to travel to the destination. As mentioned before, in large cities like New York City or Los Angeles, bike messengers are often used to take the shipment from one place to another, since logistics determine that with the traffic in large cities, it could be faster than driving. Many times, however, a personal courier will use a vehicle to transport the shipment when logistics determine that this would be the fastest way to deliver. The courier will be contacted, and will arrive to pick up the shipment, get the pertinent information, and will then drive to the destination and deliver the package or documents in person.
International courier services
Though almost all large courier services are international, there is one type of international courier service that stands out as different from the rest. This is the type of courier service that employs one or two actual people to deliver the shipment by traveling to the destination personally. These people are called "international couriers", and they add a much more direct and personal touch to the delivery. Becoming an international courier can take some time, but the couriers themselves often find this type of work very rewarding. When you are employed as an international courier, you often get to travel to many different types of places for free, or for a greatly reduced cost. Though a large percentage of the time most international couriers do not deliver packages or documents overnight or express, there actually are times when they have to travel at a moment's notice in order to deliver a shipment within a very short time. Many people, if the logistics of their lives allow for this type of travel, find it a very exciting way to travel, or even make a living.
historical background
Courier or postman, Japan, hand-coloured albumen print by Felice Beato, between 1863 and 1877.

Courier or Bicycles postman, America, year 1912.
In past times, before there were vehicles, couriers were usually just individual messengers, who traveled from one place to another to deliver news, documents, or products to the destination. Examples of this were the courier services of medieval times, which were one or more people who delivered messages or goods on horseback, or the famous pony express riders, who relayed messages or goods across the United States by passing them along from rider to rider until they reached their destination. Courier services, as well as trains also used stagecoaches after they started coming into regular use. As time progressed and the age of technology set in, courier services began to use vehicles such as automobiles, modern trains, and airplanes
Historical background courier serves in United States
The courier industry has long held an important place in United States commerce and been involved in pivotal moments in the nation's history such as westward migration and the gold rush. Wells Fargo was founded in 1852 and rapidly became the preeminent package delivery company. The company specialized in shipping gold, packages and newspapers throughout the West, making a Wells Fargo office in every camp and settlement a necessity for commerce and connections to home. Shortly afterward, the Pony Express was established to move packages more quickly than the traditional method, which followed the stagecoach routes. It also illustrated the demand for timely deliveries across the nation, a concept that continued to evolve with the railroad , automobiles and interstate highways and which has emerged into today’s courier industry.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transportation
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Courier
Major Player/Organization, Market Size, Market Trends, Changes in Courier Industry, Current ICT/IS Adoption and Benefits - Khadijah

Source: Infobase Marketing Courier Market Size Model
Courier industry had been broken down into two major segments – Overnight or Later Delivery and Sameday or Messenger.
a. Overnight or Later Delivery
Shipments that are delivered at least one day after the day they are picked up. This segment of the market includes shipments delivered within Canada, to the United States or other countries around the world.
b. Sameday or Messenger
Shipments that are delivered the same day they are picked up. By definition, these tend to be primarily local and/or regional deliveries.

Source: Infobase Marketing Courier Market Size Model
As we can see from the chart above, overnight or late deliveries represent the majority of the market in year 2000. This is due because of the duration and time needed to deliver which contributes to the different share of revenue and volume.
Market Trends
Pace in the activity had been slowing down in the early 2000. However with the decision made by Federal Express to absorb Roadway Package System (RPS) in their operation, challenge had been increasing from other companies as this type of technology attract a lot of customers. VIA Rail Canada also had been used VIAPAQ courier service which also contributes to the high competition in Courier Industry.
Many services have developed over the past year whose primary purpose is to bring together shippers and transportation companies on the internet. Examples include GoShip.com, GoCargo.com and iLinkGlobal.com. While each of these services do in fact perform physical pickup and delivery, many of the traditional “bricks and mortar” support services and infrastructure are avoided due to the internet. For courier companies, it will be increasingly important to ensure they are listed as an option in these types of services thus increases their customers.
Increasing trade liberalization throughout the world and continued economic development and growth among less-developed nations are creating a need for more and more international shipping. While the major integrators are rushing to be the first into these new market areas and/or increase their capabilities, this also creates an opportunity for domestic players. Specifically, several opportunities may exist to serve as an interline or delivery agent for major domestic players in markets abroad.

Source : Infobase Marketing Courier Market Size Model
Prices in the courier industry have been on an upswing over the past several years and are in fact expected to continue to do so into the foreseeable future.

Source: Transport Canada Policy Group
Internet purchases by businesses in the U.S. are forecast to be $1.5 trillion by 2004. Business to consumer e-commerce is also significant, and forecast to grow from its current level of about $8 billion to $184 billion over the same period.
Using a Canadian conversion factor that assumes Canada represents 10% of U.S. activity, the value of the Canadian business-to-business internet market will be almost $200 billion annually by the year 2004. Using research conducted by Ernst & Young, which suggests the average transaction purchase value on the internet is $92.00 (U.S.), and assuming an average revenue/shipment for these purchases of $6.00 (Journal of Commerce, 2000), this would suggest the size of the courier-related shipping market in the U.S. in 2000 was $3.0 billion.
For courier companies, the shift away from larger shipments, distribution centres and retail locations to direct delivery models of individual purchase shipments has the potential to drive growth to double digit figures for some time to come. The primary implication for couriers will be to develop a method to complete these deliveries to the homes of consumers since many large companies now prohibit the delivery of personal purchases to their premises in a cost-effective manner. Some, such as FedEx, are going to be adopting a strategy that will focus primarily on the business using internet which is expected to be completed online represents even higher growth than personal transactions.

Source: Infobase Marketing Courier Market Size Model
Changes in Courier Industry
Everything around us has been evolving to become more reliable and convenient nowadays including the Courier Industry. A lot of factors had been taken due to the dramatic growth of new markets which contribute to this evolution like safety of the delivering goods, demand of the consumer and technology being used for delivering purpose. How technologies help with today’s Courier Industry? One of the most contributing factors that had been making a lot of changes in Courier Industry is technology. Long ago, whenever people wanted to make delivery of goods or mails, a lot of processes need to be done such as:
1. Write or wrap the letter and items that you want to send
2. Go to the nearest post office
3. Line up to buy stamps or get form for delivery purpose
4. Paste stamps and fill in the forms of your mail
5. Pay the amount needed to do the delivery
6. Inspection of items to the required destination by the workers
7. Delivered the items to the required destination by the workers
The duration for the manual processes involved above normally takes between 3 to 7 days. But now, with the enhancement of technology in the Courier Industry, the processes of delivery become simpler and save time. Although there are some of the processes remain same but there are getting better and simpler. For example the duration of the delivery items have been shorten to 1 day and the process of delivering items become smooth without taking longer time as the need to use counter as medium to send item had been minimizing used.
Advanced technologies and faster types of transportation like jet and airplane had been utilized to realize the demands of the consumer. If long ago Courier Industry used ship or bicycle to make deliveries which took a long time of delivery, now most companies and individuals prefer using airplane or jet which shortens more time to deliver their parcels.
Current ICT/IS Adoption
Some of the famous technology that has been used widely now in the Courier Industry is RFID. RFID is being used for recording delivery, orders online and postal services.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is the reading of information on small devices using radio frequencies or thereabouts. It largely avoids the problems of human error and cost, of disorientation, obscuration and needing to read many at a time that plague barcodes, phosphor dots, print and other alternatives in the postal and courier service. It is an enabling technology of incredibly broad applicability. This is why RFID is already used in the postal and courier service for secure access by people to vehicles and secure areas, secure access of vehicles to yards, location of parcels, conveyances, trailers and much more besides. RFID monitors the performance of the letter post, matches letters to postal boxes to prevent errors and records when and how much a sensitive package has been overheated in transit. In Sweden it is the basis of smart packages that record time of tampering and theft and leads to arrests.

Source: IDTechEx
Reports had been estimated that the global market for using RFID systems will be $3 billion in 2016. It could be much bigger if current efforts to tag individual items gain widespread acceptance. In due course, over one trillion postal items will be tagged yearly, making this the second largest application of RFID in the world after the retail supply chain.
RFID is an idea whose time has come in postal, courier and high volume light logistics. In the past, RFID has been used for little more than the evaluation of postal performance, using tags in a small percentage of letters and the tracking of a small number of conveyances and vehicles. There is even a postal RFID system that completely automates the whole process of mail delivery from accepting the package to classification and dispatching. The current postal package unified information system uses barcodes, thus necessitating human effort at every mail center to input mail numbers into the system. This results in inaccuracies during transfer of duties and it delays the mail dispatches.
The new RFID system which developed by ETRI of Korea, aims to reduce costs, errors and tedious human intervention. It is difficult to estimate when pervasive RFID tagging of most of the courier and letter post will occur but RFID enabled parcels, conveyances, vehicles and trailers are now commonplace, with multiple paybacks often being enjoyed. RFID is enhancing security and safety and removing tedious operations. Swedish Post has a parcel that detects and records tampering using RFID and other innovations abound including RFID cards controlling driver access to postal vehicles and RFID enabled postal sorting equipment. Little wonder that companies as large as Microsoft have entered the fray. The global potential is illustrated by its decision to offer its first postal systems in Taiwan and elsewhere in East Asia.
Benefits of Technology in Courier Industry
With the developing technologies, people no need to wait for a long time just to send items or checking the delivery items. Moreover, customers also can check for their own status of delivery items whether had been sent to the requested destination or not. With the enhancement of technology, everything had become easier and thus gives benefit to the customers. Customer need not to fear that their parcels may not reach requested destination on time.
Reference
IBISWorld (2008). Courier Services in Australia - Industry Report. 5th February 2009. http://www.ibisworld.com.au/industry/retail.aspx?indid=503&chid=1&test=2
Roxana Grigorean (2008). Spree of acquisitions on courier service market. 5th February 2009. http://www.zf.ro/zf-english/spree-of-acquisitions-on-courier-service-market-3095009/
Roxana Grigorean (2007). Courier service companies consider 10% rate hike. 5th February 2009. http://www.zf.ro/zf-english/courier-service-companies-consider-10-rate-hike-3067103/
Transport Canada Policy Group (2006). Canadian Courier Market Size, Structure and Fleet Analysis Study. 5th February 2009. http://www.tc.gc.ca/pol/EN/Report/Courier2001/C2.htm
IDTechEx (2009). RFID in the Postal and Courier Service. 7th February 2009. http://www.idtechex.com/research/articles/rfid_in_the_postal_and_courier_service_00000338.asp
Electronics.ca (2009). RFID for Postal and Courier Service 2008-2018. 7th February 2009. http://www.electronics.ca/reports/rfid/postal_courier.html
Tuesday, February 3, 2009
Problems/ Opportunities in Courier Services(Final Version) - Lionel Lam
The dawn of electronic commerce has presented the courier industry with its fair mix of problems and opportunities, intertwined at some point of the evolution chain. From the ancient times, men have always sought the help of animals, or transportation so to speak, to assist with the transportation and delivery of goods. Today, the services of messenger pigeons and horse-drawn carriages have long gone down the gutter of history, largely because of the paradigm shift that the transportation industry had undergone, and is still undergoing as this article is written. In this article I would be touching on the problems, or opportunities, or both, presented before the courier industry.
When Opportunities Knock on your Door...
Organizations like Google, ebay, Amazon and Yahoo rely solely on IT to drive their business. These companies minus IT become dysfunctional. FedEx, WalMart and Dell have made IT an important element of their competitive advantage. Take away IT, some or all sources of competitive advantage ceases to exist. Firms like Jet Blue1, Infosys and Salesforce.com have made IT a critical element of their business model to virtualize people, process and technology respectively. Shutting out IT in these firms brings their business model to nought. IT does transform the way businesses are conducted (Prem, H. and G. E. Matthew (2006) ).
The use of technology and IT infrastructure in today's largest companies and organizations is rather 'mainstream', meaning that IT has now become an indispensable part of any organization aspiring to be successful in these highly turbulent times. Because of the important role IT plays in organization, it is recognized as an essential component in value chain analysis, where it is necessary in order to generate substantial margins for the organization concerned.
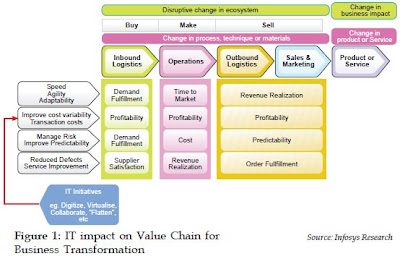
For example, when $32 billion FedEx Corporation delivers 6 million packages around the world every day, it is reaping the benefits of creating the world’s first real-time package tracking system that drives effectiveness in its delivery model. One of the key secrets of Walmart’s success is that it leverages an in-house data warehouse that maintains ten terabytes of point of sale data. This analysis helps Walmart better understand what is happening, and what did happen, within the company, leading to a tangible value for better decision making. The historic data speaks of good and bad decisions made in the past, and how much of what sells and what doesn’t sell. Furthermore, Walmart is investing heavily in technologies like RFID to bring in visibility in the changes in the demand. Capital One, one of the world’s largest providers of MasterCard and Visa credit cards, with about 44 million customers, more than 20,000 employees, is a classic example of how IT can drive efficiencies through technology innovation. It has one of the world’s best business intelligence systems that help the company not only pin point demand, but also helps it to up sell and cross sell effectively (Prem, H. and G. E. Matthew (2006) ).
The Evolution of EDI for Competitive Advantage: The FedEx Case
From the early days of e-commerce (electronic commerce), EDI was the 'in thing', and Federal Express Corporation (FedEx) was among the first few companies to see the explosive powers of e-commerce. FexEx did successfully utilize EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) to solve many problems in their complex business.
EDI was an early method of e-commerce that worked similarly to the telephone in many respects. Usually, a two-way communication link is established in EDI, typically between two trading partners. EDI requires programming on part of both trading partners in order to establish communications standards (Ayers, J. B. (2001)). In order for both companies to utilize EDI, both are required to utilize a Value Added Network (VAN), which charges a fee for information and data transmitted over the network.
In spite of the fact that e-commerce has evolved a lot in the past decades, from the humble EDI to the full-fledged e-commerce solutions that we see driving some of the most sophisticated companies today, many companies which invested heavily in EDI in the past have not resorted to scrapping their networks, instead opting to combine the old with the new to create a more flexible system. FexEx, being both a leader in technology and one of the most respected companies in the world. has found the advantage of using EDI, regardless of it's form. In addition to its continued use of EDI to support primary business functions, FedEx has developed internet solutions to assists its customers, vendors and other members in the supply chain to better interact with the company.
Advantages of EDI:
1. No human intervention is required once programming has been completed.
2. Empowers companies to better deal with inventory-related problems, should they arise.
3. Provides a platform to develop solutions for managing inventory.
4. Lowers carrying cost of inventory for companies.
Disadvantages of EDI:
1. High cost.
2. Time required for programmers to develop system and requirements.
3. Lack of in-house expertise to deal with problems that may arise.
4. Lack of common standards. Companies are unique and employ different standards.
5. No allowance for data synchronization.
6. Provides transmission of data via value added networks or internet only.
The Internet-based EDI
EDI has continued to work well with businesses that have committed the resources to keep their expensive networks running. The increasing globalization of business has forced many organizations to adopt less expensive methods. As EDI has to be complemented by other methods of communication such as the fax machine, phone, or email, errors are prone to happen. The internet therefore, is seen as an alternative, forcing changes on the traditional EDI as it evolves into a more complex yet more usable tool. Most companies have, as a result, opted to combine the two, allowing them to compete neck-to-neck with much larger competitors.
Demands and Pressures on the Courier Industry
So far we have been discussing primarily the opportunities (and some problems) that have occurred in the courier industry and the transportation industry in general. In this section, we will be covering some issues concerning the demands and pressures on the aforementioned industry, some of which are driving forces behind the industry, forcing change and creating more opportunities in this extremely challenging economic outlook.
The Concept in Brief
The years that followed the industrial revolution have seen exponential growth in the economies of countries that now make up the world's top economies. The surge in demand for supplies and commodities such as crude oil, palm oil and other materials necessary for the hungry economies of the day placed enormous strain on export countries as they struggle to keep up with intensifying demand of such commodities. However challenging the situation was in those days, companies managed to adapt the the change in paradigm, and with the advent of automation and computerization, logistics took a turn for the better. This has greatly aided and enhanced the courier industry.
According to Clarke, J.-P. (2004) in his journal "Air Cargo Economics", the biggest factors that contribute to the demand and pressure in the air cargo (or air courier / courier) industry are as follows:
1. Economic growth and trade (imports/exports).
2. Relative prices of air cargo versus alternatives (ocean, truck, rail etc.)
Growing Economies Pose Both Challenges and Opportunities
Economic growth is attributed to the growth and development of a nation's economy, and a relatively easy way to gauge the development of the economy is to monitor the exports and imports of the country. For example, countries such as India, China and Korea have exhibited extraordinary growth in exports (and of course, imports) over the last twenty years, thus placing enormous strain on the courier services offered at the time. This strain is a form of 'pressure', forcing courier companies such as FedEx and DHL to change their business methodology, and even business model, to cope with this surge in demand. Many of these companies have turned to Information Technology to add more value to the services currently being offered, in addition to serving as a differentiating factor in their business, as a way of generating substantive profit margins as well as preserving their competitive edge.
In order to remain a cut above the rest, courier companies such as FedEx, DHL and TNT have successfully capitalized on the growth of economies worldwide. Statistics show that on average, there is a 2% to 2.5% increase in world trade for each 1% increase in total GDP. An aspect that cannot be ignored is the fact that air freight trade has been growing even faster, due to regional differences in economic growth. Also, since the year 1993, there has been an average of 7% to 10% annual growth in world air freight traffic.
From a perspective of economics of scale, most would agree that air freight is still the most economical way to ship goods from one place to another, with consideration given to the time taken to undertake the shipment. Although the price for the man on the street may seem rather steep, one has to consider this fact: time is money, and courier companies have done a pretty good job in filling in this void, thus making global trade easier than ever before.
The Scourge of Globalization
Globalization, in all respects, is a phenomena that is inevitable, in that it cannot be avoided. Just as did the introduction of the automobile see the demise of traditional methods of transportation (please refer to the history section), globalization will forever change the way people on a global scale interact with one another. Companies, businesses, organizations and all, will see changes in the way they conduct business, and like many paradigms that have come and passed before, there will be challenges that these organizations must be ready to face.
The DHL Story
Few companies have better knowledge of customs rules and procedures, 'red-tapes' and misfunctionings in customs control than international courier companies. This case presents DHL's account of difficulties in serving clients across borders and around the globe (Aharoni, Y. (2000)).
DHL is the world's largest international express carrier, generating about 40 percent of the world supply of such services. The company was founded in 1969 and has expanded rapidly, establishing over 2,300 service centres in over 220 countries, and employing more than 55,000 people worldwide.
Speed and reliable delivery are essential in today's international trade business since time became a major competitive factor. It became absolutely necessary for companies on such a large scale to manage their supply chain (and value chain) effectively, hence the necessity to employ information technology in the business processes.
DHL handles more than 100 million shipments per year with the world-renowned 'hub and spoke' network of planes, trucks and infrastructure. In order to maintain its lead in this very competitive market-place, the company focused on quality and speed of delivery.
This story is not just a story about a very successful company in this industry, but it is also a brilliant example of how an organization successfully capitalizes on the opportunities available, as well as one that carefully identifies the pressures and demands placed on it in this increasingly borderless world.
Customer-Driven Changes
In this time of fast-paced economic growth, a key player in driving change is undeniably the customer themselves. Clarke, J.-P iterates that the number of 'just-in-time' deliveries have risen dramatically over the year, prompting courier companies to offer fast and efficient delivery services specifically to cater to this demand. Obviously some of the other external factors also nestles on how customers choose to shop. The coming of eBay and Dell, for example saw the need for 'quick and instant gratification', so courier services and companies had to adapt to quickly embrace this new segment of customers. Needless to say, companies that failed to see this golden opportunity would see an eventual demise
References:
Journal articles:
Jiang, B. and E. Prater (2002). "Distribution & Logistics Development in China:
the Revolution has begun."
Savage, B. M. (2003). "America’s Transportation Network: The Next Revolution."
Prem, H. and G. E. Matthew (2006). "How IT Enables Business Transformation?"
Clarke, J.-P. (2004). "Air Cargo Economics."
Books:
Ayers, J. B. (2001). Making Supply Chain Management Work. Design, Implementation, Partnerships, Technology and Profits, Auerbach Publications.
Aharoni, Y. (2000). Globalization of Services: Some Implications for Theory and Practice Routledge.
Web Pages:
"Wikipedia - Value Chain Analysis." Retrieved 4th February 2009, from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Value_chain.
Work Delegation - Assignment 2
-problems faced (Lionel)
-opportunities (Lionel)
-historical background (Aziz)
-current scenario (Kar Teck)
-major player/organization (Dja)
-market size (Dja)
-demands (statistics), pressure (Lionel)
-current ICT/IS adoption (Dja)
-future (Kar Tck)
-conclusion (Kar teck)
-refs
Saturday, January 17, 2009
Transportation in Courier Industry (Full)
What is Courier?
Courier companies used transportation as they’re main business. The basic definition of "courier" is simply someone who delivers something from one place to another place. A courier is a messenger, conveying something of importance from the sending source to the receiving source. They provide services to companies and individuals who need rapid service, accountability, and tracking that regular mail does not accommodate. Within this definitive context, couriers and courier services can come in many different types and styles.
Transportation in Courier Industry
In past times, before there were vehicles, couriers were usually just individual messengers, who traveled from one place to another to deliver news, documents, or products to the destination. Examples of this were the courier services of medieval times, which were one or more people who delivered messages or goods on horseback, or the famous pony express riders, who relayed messages or goods across the United States by passing them along from rider to rider until they reached their destination. Courier services, as well as trains also used stagecoaches after they started coming into regular use. As time progressed and the age of technology set in, courier services began to use vehicles such as automobiles, modern trains, and airplanes.

Pressure and Demand on the Courier Industry
The years that followed the industrial revolution have seen exponential growth in the economies of countries that now make up the world's top economies. The surge in demand for supplies and commodities such as crude oil, palm oil and other materials necessary for the hungry economies of the day placed enormous strain on export countries as they struggle to keep up with intensifying demand of such commodities. However challenging the situation was in those days, companies managed to adapt the the change in paradigm, and with the advent of automation and computerization, logistics took a turn for the better. This has greatly aided and enhanced the courier industry.
The Paradigm of Economics according to the economic model of supply and demand, the stronger the demand for one particular commodity, the higher the price will be. But sometimes, it is true the other way round. If you have been reading the part on the history of the courier, you may understand that in the past, it was very expensive to afford such services and for much part this is esteemed to be a luxury. The physical strain placed on the industry was just too much to handle, and in order to survive such turbelent times, it was deemed necessary for the courier industry to embrace computerization to:
1. Reduce operating expenses
2. Promote reliability of services
3. Improve reputation.
Living in a Pressure Cooker...
Living in such pressing times calls for drastic measures oftentimes. Some of the common cited pressures and demands are caused by the following:
1. Increase in number of competitors
2. The need to have products and commodities delivered on time, and in one piece
3. A growing number of sectors are increasingly supported by mission-critical services. Example, Singapore's Domestic Speedpost Islandwide (an offshoot of Speedpost Express) delivery helps delivers common goods to clients to any location within Singapore in the same day.
4. The paradigm change from product orientation to customer/service orientation. In other words, customer satisfaction is priority number one.
Technology and Changes in Courier Industry
Everything around us has been evolute to become more reliable and convenient nowadays including the Courier Industry. A lot of factors had been taken due to the dramatic growth of new markets which contribute to this evolution like safety of the delivery goods, demand of the consumer and technology being used for delivering purpose. How technologies help with today's Courier Industry? One of the most contributing factors that had been making a lot of changes in Courier Industry is technology. Long ago, whenever people wanted to make delivery of goods or mails, a lot of processes need to be done such as:
1. Write or wrap the letter and items that you want to send
2. Go to the nearest post office
3. Line up to buy stamps or get form for delivery purpose
4. Paste stamps and fill in the form of your mail
5. Pay the amount needed to do the delivery
6. Inspection of items being done manually
7. Delivered the items to the required destination by the workers
The duration for the manual processes involved above normally takes between 3 to 7 days. But now, with the enhancement of technology in the Courier Industry, the processes of delivery become simpler and save time. Although there are some of the processes remain same but there are getting better and simpler. For example the duration of the delivery has been shorten to 1 day and the process of delivering items become smooth without taking longer time as the need to use counter as a medium to send item had been minimizingly used.
Advanced technologies and faster types of transportation like jet and airplane had also been utilized to realize the demands of consumer. If long ago Courier Industry used ship or bicycle to make deliveries which took a long time of delivery, now most company and individuals prefer using airplane or jet which shorten more time to deliver their parcels.
Changes and benefits of technology in Courier Industry
Some of the famous technologies that had been used widely now in Courier Industry are RFID and Computerized Tracking. RFID is being used for recording delivery, orders online and postal services purpose while Computerized Tracking used to identify and trace the requested goods. With the developing technologies, people no need to wait for a long time just to send items or checking the delivery items. Moreover, customers also can check for their own status of delivery items whether had been sent to the requested destination or not. Now everyone can do it online with a faster and convenient way anytime.
The Future of Courier Industry
To sum it up, courier service is transformed and enhanced to meet the needs and demand of the current market by implementing latest technologies including Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). Courier service is a potential business model that could be enlarged and expanded to generate more revenue in future.
Couriers will specialize in delivering important or sensitive packages that need to be received in the local area; and/or because of time and temperature concerns, such as organs for transplant or key equipment or parts that are necessary for day to day operations. Even two-day delivery services use courier firms. Items that are mis-sorted, forgotten or just not picked up on a larger courier’s route. When a mistake has been discovered, courier firms fill in the gap and ensure packages are delivered on time.
In future, demand for a new type of representative courier will be emerged. With the increase in fuel prices and productivity goals monitored closely by companies, this new type of all-in-one courier has developed to "take care of business". Workers in companies have more work and less time to be out of the office. Operating largely using independent contractors that have gone through a screening process and background checks have found a niche in the courier industry. Research, in transit pet care, complex paperwork filing, and a host of other services are now offered in this new category of courier service. Under the current financial climate the trend has seen corporate businesses evaluate courier costs and steer away from sameday couriers and tend to sway towards the cheaper next day delivery solution.
In fact, courier firms specializing in same-day delivery provide an invaluable service because the "big five" (Aramex, DHL, FedEx, TNT N.V., and UPS) in the delivery business simply do not provide same-day delivery services uniquely designed to meet specific individual customer needs. Expedited delivery firms also prevent the big five from having a complete monopoly on deliveries that must be completed in a short period of time. This competition, both among couriers and with the big five, has greatly increased the quality and professionalism of the industry, while also ensuring reasonable rates for customers.
References :
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Courier http://www.electronics.ca/reports/rfid/postal_courier.html http://rfid.idtechex.com/research/reports/rfid_for_postal_and_courier_services_2008_2018_000129.asp
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logistical#Business_logistics http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Supply_and_demand
by : Aziz, Lionel, Khadijah and Kar Teck
Friday, January 16, 2009
my latest and final intro..i think..

intro of Transportation :
What is transportation? Transport or transportation is the movement of people and goods from one place to another. The term is derived from the Latin trans ("across") and portare ("to carry"). Transports have many categories such as Animal-powered transport, Aviation, Cable transport, Human-powered transport, Hybrid transport and Ship transport. Industries which have the business of providing equipment, actual transport, or goods and services used in transport of goods or people make up a large broad and important sector of most national economies, and are collectively referred to as transport industries.
Intro of Courier :
Courier companies used transportation as they’re main business. The basic definition of "courier" is simply someone who delivers something from one place to another place. A courier is a messenger, conveying something of importance from the sending source to the receiving source. They Provide services to companies and individuals who need rapid service, accountability, and tracking that regular mail does not accommodate. Within this definitive context, couriers and courier services can come in many different types and styles.

